Film piracy has become a persistent threat to the global entertainment industry, costing billions in revenue loss each year. As digital access expands, so do the methods of illegally distributing and consuming copyrighted content. From unauthorized streaming websites to peer-to-peer (P2P) file-sharing networks and social media piracy, illegal movie distribution has become more sophisticated. It is increasing making it difficult for filmmakers, production houses, and streaming platforms to protect their intellectual property. While piracy often seems like a harmless act to consumers seeking free content, its impact is far-reaching. Movie piracy is affecting not only major studios but also independent filmmakers, actors, technicians, and the broader film ecosystem.
Table of Contents:
- What is Film/Movie Piracy?
- Understanding Film Piracy: A Growing Crisis in the Digital Age
- The Economics of Piracy
- Online Digital Piracy in the Film Industry
- Copyright Laws on Film and Digital Piracy in India and Worldwide
- The Dangers of Pirated Content
- Piracy Trends in Asia-Pacific: A Shift Towards Social Media Platforms
- VdoCipher’s Anti-Piracy Measures & Hacker Identifications Tools
- FAQs
What is Film/Movie Piracy?
Film piracy is when people watch, download, or share movies illegally without paying for them. Imagine a filmmaker spends years creating a movie, hiring actors, renting equipment, and promoting the film. The only way to recover these costs and make a profit is through ticket sales in theaters or subscriptions on streaming platforms.
Now, suppose someone sneaks into a theater, records the movie on their phone, and uploads it to a website where anyone can watch it for free. Instead of buying tickets or subscribing legally, people start watching this pirated version. As a result, the filmmakers and everyone involved in making the movie lose money, which affects future productions.
Another example is when someone buys a single streaming subscription and shares their login with multiple people, or when websites offer free downloads of movies that are meant to be paid for. These actions may seem small but, when done at a large scale, they cause huge financial losses to the film industry.
| Legal Access | Illegal Access (Piracy) |
| Viewers pay for a movie ticket or subscription | Viewers watch for free through pirated sources |
| The filmmaker earns money from each ticket sold or subscription |
The filmmaker loses revenue as the movie is shared without permission
|
| Content is protected by copyright and DRM |
The content is illegally downloaded, recorded, or streamed without protection
|
| Streaming services or theaters are licensed distributors |
Pirated websites and apps are unauthorized distributors
|
Understanding Film Piracy: A Growing Crisis in the Digital Age
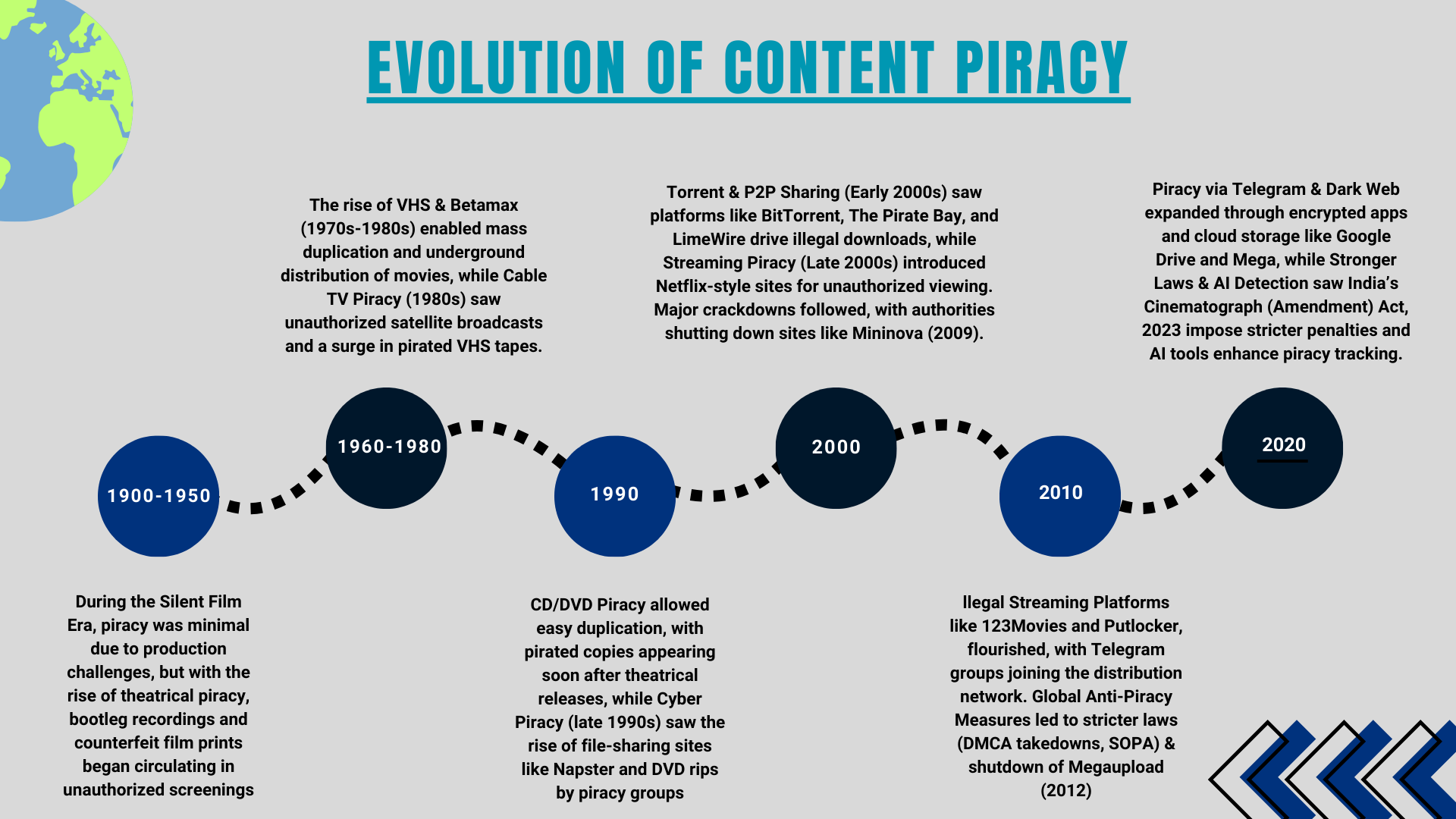
Film piracy is the unauthorized reproduction, distribution, or sharing of movies without the permission of the copyright owner. It includes various illegal activities, including recording films in theaters, duplicating and selling physical copies, and distributing pirated versions through digital platforms.
Piracy circumvents legal distribution channels, allowing individuals to access movies without paying for them, which results in substantial financial losses for filmmakers, production houses, and distributors.
Online video piracy has become the most prevalent form, where high-quality movie rips are uploaded and shared within hours of a film’s release, significantly undermining the revenue of both theatrical and OTT platforms. Beyond economic damage, piracy also fuels cybercrime, exposes users to malware and data theft, and discourages investment in original content creation.
To truly understand the depth of film piracy, it’s essential to understand its various forms:
1. Theatrical Piracy: The Oldest Form of Film Theft
One of the most common and damaging methods of piracy is camcorder recording inside theaters, often referred to as “cam rips.” In this practice, individuals use handheld cameras, smartphones, or even hidden recording devices to capture a movie directly from the screen. These low-quality recordings, often featuring poor audio, distorted visuals, and audience noise, quickly find their way to piracy websites and illegal streaming platforms within hours or days of a film’s release.
- Immediate revenue loss for filmmakers, especially in the critical opening weekend.
- Reduced audience turnout as potential moviegoers opt for free, pirated versions instead of purchasing tickets.
- Devaluation of cinematic experience, as many first-time viewers encounter the film in a subpar format rather than in its intended high-quality presentation.
2. Physical Media Piracy: Illegal Distribution Networks
Despite the rise of digital piracy, physical piracy remains prevalent, particularly in regions with limited internet access. This method involves the unauthorized duplication and sale of films through:
- DVDs, CDs, and Blu-rays, often produced in mass quantities and sold at a fraction of the original price.
- Street vendors and black-market dealers who distribute these pirated copies in public markets.
While physical piracy may not be as dominant as it once was, it continues to thrive in developing nations where consumers prefer cheap, tangible alternatives to expensive cinema tickets or streaming subscriptions.
3. Online Piracy: The Digital Black Market
The most significant challenge facing the film industry today is online piracy, driven by the ease of digital distribution. This category includes:
- Torrent sites (e.g., The Pirate Bay, 1337x, YTS) that allow peer-to-peer (P2P) file sharing of movies in high-definition.
- Unauthorized streaming platforms mimicking legitimate services like Netflix or Amazon Prime, offering free access to copyrighted content.
- Illicit Telegram groups, social media pages, and dark web sites, where users can download or stream newly released films within hours of their theatrical or OTT premiere.
Piracy is not just about free movies. It erodes the creative economy, discourages investment in new projects, and threatens the livelihood of thousands working in the film industry. Beyond financial loss, pirated platforms often expose users to malware, data theft, and cyber fraud, making piracy a risk not just for filmmakers, but for consumers as well.
How Piracy Affects Film Production Budgets and Revenues
Revenue Loss & Diminished Returns on Investment
Film production requires huge financial investments, covering expenses for cast, crew, set design, special effects, marketing, and distribution. The primary revenue sources for films include:
- Box Office Sales (theatrical releases)
- Streaming Platform Licensing (OTT platforms like Netflix, Prime Video, Disney+)
- DVD and Blu-ray Sales
- TV and Pay-Per-View Rights
When a pirated copy of a movie becomes available online, sometimes within hours of release, it severely affects these revenue streams. Viewers who would have otherwise paid for a ticket or subscription may opt to watch the pirated version for free, leading to massive financial losses for filmmakers and distributors.
Delayed Returns on Investment & Market Distortion
For major studios, piracy often results in lower-than-expected revenue projections, leading to reduced budgets for future films. For small and independent filmmakers, breaking even becomes a challenge, forcing many to exit the industry.
The Economics of Piracy
A number of non-economic arguments against piracy, focus on ethical and moral concerns, emphasizing fairness and the importance of compensating creators for their work. However, from an economic perspective, the primary concern is efficiency, maximizing overall societal benefits.
Short-Term Impact of Piracy
In the short run, once a product is created and made available in the market, the fixed costs of production (such as research, development, and marketing) have already been covered. At this stage, piracy appears to have mixed effects on the economy.
When someone who would have paid for a product (e.g., a movie or music album) chooses to pirate it instead, the creator or company loses revenue. However, the consumer gains access to the content for free. In economic terms, this transaction does not reduce overall social welfare. Instead,it simply redistributes it from producers to consumers.
On the other hand, when someone who would not have purchased the product at full price pirates it, they gain value at no additional cost to the producer. This increases overall welfare, as more people get to enjoy the product without impacting the producer’s existing revenue.
In simple words, while piracy shifts some benefits from content creators to consumers, it also expands the total number of people who can access the content, potentially increasing short-term social welfare.
Long-Term Impact of Piracy
Economists, however, are more concerned with the long-term effects, a period in which producers decide whether to invest in creating new content. This is particularly relevant in industries with high fixed costs and low marginal costs, such as movies, music, and software.
For example, blockbuster films often require hundreds of millions of dollars in production and marketing costs. If piracy reduces the expected revenue of these films to a level below their production cost (including an acceptable profit margin for investors), studios may decide that producing such films is not financially viable. This results in fewer films being made, ultimately reducing choices for consumers and shrinking overall social welfare.
In this scenario, piracy harms both producers and consumers. Producers lose revenue, and consumers miss out on new content that might never be created due to financial risks.
The Core Economic Debate
The argument for strict copyright protection is based on two key assumptions:
- Piracy reduces revenue for artists and media companies – A claim strongly supported by academic research. A review of 23 peer-reviewed studies found evidence that piracy negatively affects sales, while only three studies found no impact.
- Lower revenue leads to a decrease in creative output. This remains a debated issue.
- While some argue that financial losses discourage new content creation, others believe that alternative funding models (such as streaming subscriptions, crowdfunding, or merchandising) might sustain content production despite piracy.
The key unresolved question in copyright economics is whether piracy truly stifles the production of creative works or if the industry can adapt and continue to thrive despite it. This ongoing debate shapes policies around copyright enforcement and digital rights management.
Online Digital Piracy in the Film Industry
The traditional notion of piracy, once associated with plundering ships, has evolved into a modern-day digital issue, the unauthorized copying and distribution of online content. Digital piracy spans various media, including movies, music, video games, and e-books. Film piracy, a significant aspect of digital infringement, involves accessing, sharing, or duplicating copyrighted content without proper authorization, whether for personal use or commercial gain.
According to the IP Crime Group, piracy encompasses the illegal reproduction and distribution of copyrighted materials such as films, sports events, literary works, and software. This is largely facilitated by P2P (peer-to-peer) networks, streaming platforms, aggregator websites, and ISPs that allow users to share and access pirated content. Media piracy generally involves either downloading movies illegally from the internet or making unauthorized copies from DVDs or streaming services to distribute further.
Globally, copyrighted films are made available illegally through multiple channels, including:
- Subscription-based OTT platforms (often bypassed via illegal account sharing or cracking).
- Cyberlockers that store and distribute pirated content.
- Ripped content from cinemas, Blu-ray discs, iTunes, and OTT services, later shared via platforms like BitTorrent, Dailymotion, and Telegram.
- Illicit rebroadcasting of TV and live-streamed content from local television stations.
Despite advancements in content distribution, piracy remains rampant due to unauthorized recordings in cinemas and third-party software that extracts content from streaming services. P2P file sharing emerged with Napster, later leading to decentralized file-sharing platforms such as Gnutella, FastTrack, and BitTorrent, which operate without centralized control, making regulation difficult.
In January 2025, the documentary “Selena y Los Dinos” was removed from the Sundance Film Festival’s streaming platform due to copyright infringements. Viewers recorded parts of the film and posted them on social media platforms like TikTok and Instagram, leading to its removal. This incident highlights the challenges filmmakers face in protecting their work in the digital age.
Streaming piracy has further expanded, with sites like 123Movies and unauthorized Telegram groups facilitating illegal content distribution. Typically, pirated versions of films become available within weeks of release, sourced through methods like CAM recordings, TC (Telecine) rips, and DVDRips/BluRay leaks.
BitTorrent remains the most dominant file-sharing technology globally, enabling users to share files regardless of size or format. The past decade has seen the rise of additional software tools and private chat-based sharing platforms like Telegram, which offer unlimited cloud storage for piracy. India is a major contributor to global P2P file-sharing traffic, as highlighted by the Motion Picture Distributor Association (MPDA).
Piracy undermines revenue generation and tax collection, as illegal copies often reach audiences before official releases in cinemas or OTT platforms. However, internet service providers (ISPs) lack control over these transmissions, leading to legal ambiguities in holding them accountable. As piracy continues to evolve with technology, enforcing regulations and implementing robust anti-piracy measures remains a significant challenge for the Indian film industry.
Effects on Independent Filmmakers vs. Big Studios
While piracy negatively impacts both big-budget blockbusters and indie films, the effects are far more devastating for independent filmmakers:
| Factor | Big Studios (Hollywood, Bollywood, etc.) | Independent Filmmakers |
| Financial Reserves | Have large budgets & multiple revenue streams |
Limited budgets, high dependency on box office
|
| Marketing Power | Can recover losses through global distribution |
Limited reach; piracy cuts potential profits
|
| Legal Action | Have legal teams to fight piracy |
Cannot afford costly lawsuits
|
| Audience Impact | Fans still go to theaters for the “cinematic experience” |
Viewers often opt for pirated versions due to limited availability
|
For example, Marvel or Warner Bros. might still generate revenue despite leaks, but an indie film at a film festival may never get a proper theatrical release if pirated early.
Impact on Jobs in the Film Industry
Film piracy doesn’t just hurt producers and studios, it affects everyone involved in filmmaking, including:
- Actors & Directors – Reduced revenue means fewer high-budget projects, leading to fewer acting and directing opportunities.
- Writers & Screenplay Artists – Lower film profits lead to fewer commissioned projects, affecting scriptwriters and screenwriters.
- Crew Members – Cinematographers, set designers, costume designers, and VFX artists are directly impacted when budget cuts reduce hiring.
- Post-Production Teams – Editors, sound engineers, and production assistants lose work opportunities when studios cut costs.
- Distributors & Theater Owners – With fewer people buying tickets, theaters struggle to stay profitable, leading to job losses in cinema chains.
The decline in theater revenue due to piracy contributed to the closure of many single-screen theaters in India, impacting local businesses and jobs.
Copyright Laws on Film and Digital Piracy in India and Worldwide
Movie copyright laws exist to protect the rights of filmmakers, production houses, and content creators, ensuring that their work is not used, copied, or distributed without authorization. Copyright laws vary across countries, but they generally aim to prevent piracy and unauthorized usage while promoting creativity and fair access to content.
What is Copyright?
Copyright is a legal right granted to creators of literary, artistic, musical, dramatic, and cinematographic works. It protects original works from unauthorized reproduction, adaptation, and distribution. Copyright ensures that authors, filmmakers, musicians, and software developers retain control over their intellectual property.
Balancing Copyright Owners’ Rights and Public Interest
Copyright laws are designed not just to safeguard the rights of creators but also to ensure that society can use copyrighted materials for essential purposes like education, religious ceremonies, research, and news reporting. These uses are typically exempted under “fair use” or “fair dealing” provisions, meaning people can use copyrighted material in specific scenarios without seeking permission from the copyright holder.
What Constitutes Copyright Infringement?
A work is considered to be infringed only if a substantial part of it is used without authorization. However, the law does not define “substantial” solely based on the amount copied. Instead, it considers the quality and significance of the portion used.
Quality vs. Quantity in Copyright Infringement
A short excerpt can still constitute infringement if it represents an essential or distinctive part of the work.
Example: If a lyricist copies a memorable or iconic phrase from another song, it may be considered copyright infringement, even if the phrase is just a few words long.
This principle applies to music, literature, films, and even digital content, where a small but crucial portion can be protected under copyright laws.
Movie Copyright Rules in India
In India, the protection of movie copyrights is governed primarily by the Copyright Act, 1957, along with amendments made to align with digital advancements and global intellectual property standards. The key aspects of Indian movie copyright laws include:
1. Ownership of Copyright
- The copyright of a film typically belongs to the producer unless otherwise specified in a contract.
- Writers, directors, musicians, and lyricists also hold rights over their individual contributions, protected under moral rights provisions.
2. Duration of Copyright Protection
- The copyright for cinematographic films in India lasts for 60 years from the year following the film’s release.
- After the expiration of this period, the movie enters the public domain, allowing free usage.
3. Exclusive Rights of the Copyright Holder
The copyright owner has exclusive rights to:
- Reproduce the film in any format (DVD, Blu-ray, digital platforms, etc.).
- Distribute copies via sale, rental, or streaming platforms.
- Broadcast or public performance, including screenings in theaters and television broadcasts.
- Adapt the work into other formats, such as remakes or sequels.
4. Legal Provisions Against Piracy
- Cinematograph (Amendment) Act, 2023 introduced stricter penalties for piracy, including imprisonment of up to three years and hefty fines.
- Under the Information Technology Act, 2000, digital piracy (such as unauthorized streaming and downloads) is also punishable.
- The John Doe Order (injunction against unknown infringers) is widely used to block websites hosting pirated content.
5. Fair Use and Copyright Exceptions
- Limited use is permitted for educational, research, or review purposes under Section 52 of the Copyright Act.
- Small clips may be used for criticism or commentary, but full-length distribution without permission is illegal.
In August 2024, an international anti-piracy coalition, including major Hollywood studios and led by the Alliance for Creativity and Entertainment (ACE), collaborated with Vietnamese authorities to shut down Fmovies, one of the world’s largest illegal streaming operations. This action marked a significant victory for the entertainment industry.
Movie Copyright Rules Worldwide
Internationally, movie copyright laws are governed by various treaties and national legislations. Some of the key frameworks include:
1. Berne Convention for the Protection of Literary and Artistic Works (1886)
- Ensures automatic copyright protection across 180+ member countries.
- Recognizes the minimum duration of 50 years for film copyrights.
2. World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) Treaties
- WIPO Copyright Treaty (WCT) and WIPO Performances and Phonograms Treaty (WPPT) strengthen protection for digital media.
- Prevents unauthorized reproduction and distribution of digital content.
3. Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) – United States
- Enforced by the U.S. Copyright Office to combat online piracy.
- Websites hosting pirated content can be taken down through DMCA Takedown Notices.
4. European Union Copyright Directive
- Introduces “upload filters” that hold platforms (e.g., YouTube, Facebook) accountable for copyrighted content uploaded by users.
- Strengthens enforcement against piracy within EU member states.
5. Copyright Duration in Major Countries
- United States & EU: Copyright lasts 70 years after the creator’s death (for individual authors) and 95 years for corporate films.
- United Kingdom: 70 years after the death of the last contributing author.
- China: 50 years from the first publication.
The Japanese government and publishers have deployed AI-Powered Anti-Piracy Measures to track and remove unauthorized manga copies online in 2024
The Dangers of Pirated Content
This rapid infection rate underscores the severe risks associated with illegal streaming and pirated content. Many piracy websites act as breeding grounds for malicious software, exposing users to data breaches, financial fraud, and identity theft.
A study, “Time to Compromise,” commissioned by the Asia Video Industry Association (AVIA) and led by cybersecurity expert Dr. Paul Watters, highlights the alarming speed at which malware infiltrates devices. According to the findings:
Windows devices can be infected by an advanced persistent threat (APT) in as little as 42 seconds.
Android devices are not far behind, with malware penetration occurring within 78 seconds.
- Malware embedded in pirated content can steal passwords, track keystrokes, and gain remote access to your device.
- Cybercriminals exploit these vulnerabilities to launch phishing scams, ransomware attacks, and even access banking details.
- Pirated platforms lack security controls, making them prime targets for hackers to distribute infected files.
How Pirated Content Puts You at Risk
1. Password Theft & Identity Fraud
Malware embedded in pirated content can:
- Steal passwords by recording keystrokes.
- Gain remote access to your device and steal sensitive information.
- Compromise personal data, leading to identity theft or bank fraud.
2. Phishing and Ransomware Attacks
Cybercriminals use pirated platforms to:
- Trick users into entering credentials on fake login pages.
- Install ransomware, locking users out of their own files until they pay a ransom.
In 2023, a major ransomware attack targeted torrent users, encrypting their files and demanding cryptocurrency payments.
3. Financial Fraud & Credit Card Theft
Many illegal streaming sites trick users into entering their credit card details under the pretense of “free” subscriptions or VIP access. Once obtained, these details can be used for:
- Unauthorized transactions
- Dark web sales of financial information
4. Child Safety Risks
Piracy websites are not regulated and can expose children to:
- Explicit adult content disguised as family-friendly movies.
- Predatory threats, as many piracy platforms do not filter harmful ads or chat rooms.
5. Government & Legal Consequences
Downloading or distributing copyrighted content illegally can lead to legal action, including:
- Hefty fines for accessing pirated material.
- IP tracking and legal notices from ISPs in many countries.
- Criminal charges for hosting or distributing pirated films.
How to Stay Safe
- Use trusted content sources – Stick to legitimate streaming services.
- Update security software – Keep your antivirus and malware protection active.
- Avoid clicking suspicious links – Many pirated sites trick users with deceptive pop-ups.
- Educate yourself and your family – Awareness is the first step in preventing cyber threats.
In just a matter of seconds, your device, data, and privacy could be at risk. Prioritizing cybersecurity and ethical content consumption is the best way to protect yourself from digital threats.
“According to the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), identity theft is escalating at an alarming rate. In just the first half of 2023, more than 560,000 cases of identity theft were officially reported in the United States.”
Piracy Trends in Asia-Pacific: A Shift Towards Social Media Platforms
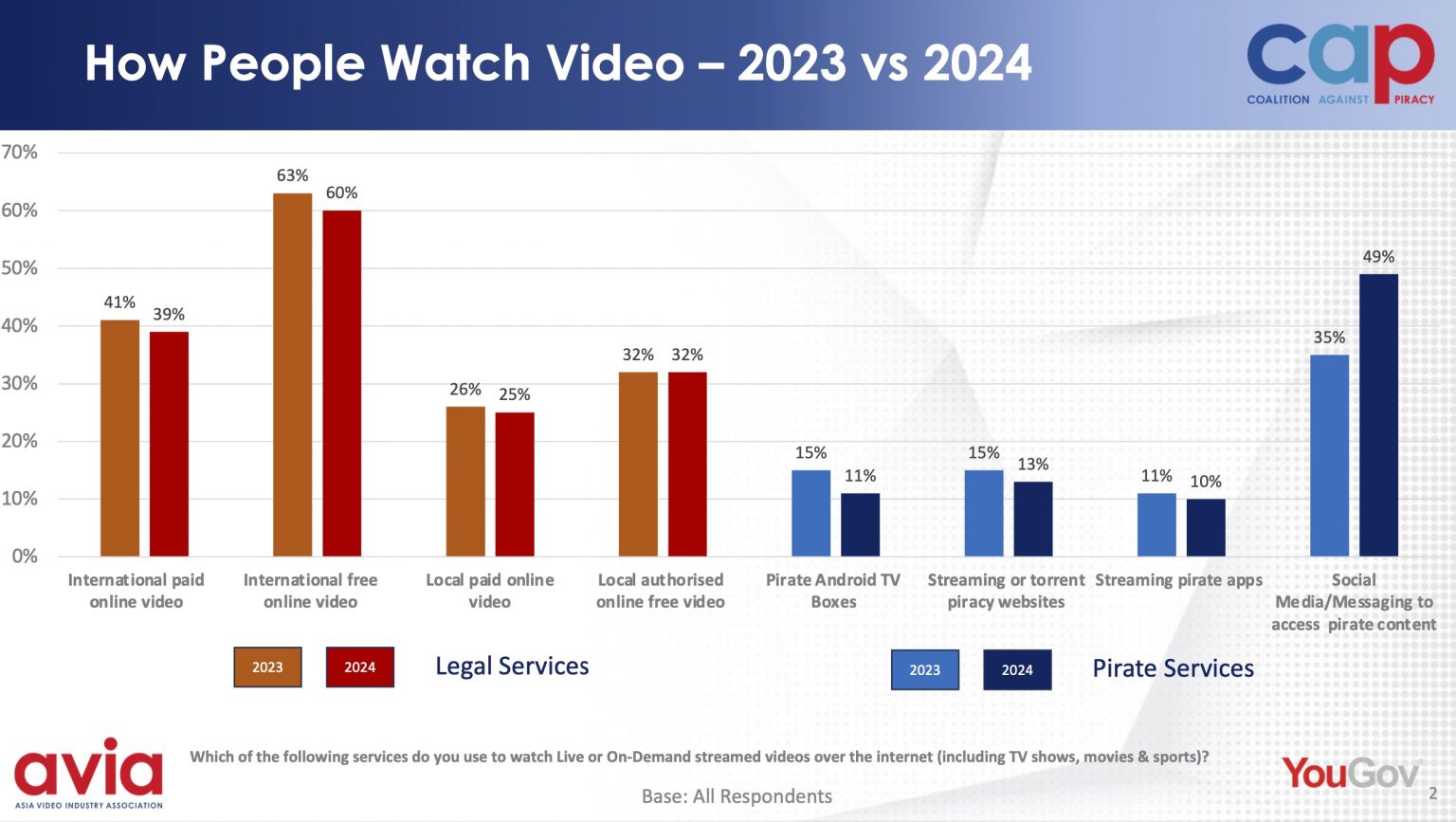
The Asia Video Industry Association’s Coalition Against Piracy (CAP) has released its 2024 annual consumer survey conducted by YouGov, revealing a concerning shift in digital piracy trends. While the use of traditional pirate TV boxes, illicit streaming apps, and torrent sites has declined, overall piracy is on the rise, now impacting 59% of consumers across the Asia-Pacific region, up from 52% in the previous year. The driving force behind this surge? An increasing reliance on social media and messaging platforms for accessing pirated content.
The report highlights alarming spikes in piracy rates in the Philippines and Vietnam, where the number of consumers engaging in piracy has risen by 12% and 13% year-over-year, respectively, pushing their total piracy rates to a staggering 70% and 71%.
- Social media and messaging apps have emerged as the dominant piracy channels, witnessing a 14% increase in usage across the region.
- Pirate websites and TV boxes are seeing a decline, with only 13% of users accessing piracy through websites and 11% using pirate TV boxes, both marking a significant drop from previous years.
Despite the rising numbers, there is a silver lining. Awareness of piracy’s negative consequences is growing. A staggering 89% of consumers recognize piracy’s impact, including its links to organized crime, the spread of malware, and financial harm to local content industries.
Image source: https://avia.org/
Anti-Piracy Enforcement and Industry Response
Efforts to curb piracy through judicial and administrative blocking of pirate sites are proving effective. Countries like Indonesia (59%), Vietnam (54%), Malaysia (42%), and Singapore (28%) have reported a noticeable reduction in piracy as a result of these measures.
The Role of Social Media and Messaging Platforms
The most disturbing development uncovered in the survey is the dramatic rise in piracy through social media and messaging platforms. CAP continues to collaborate with major tech companies to combat piracy on these platforms, but Telegram has been identified as a major concern due to its lack of cooperation.
| Country/Category | Statistics |
| Philippines | 70% piracy rate (+12%) |
| Vietnam | 71% piracy rate (+13%) |
| Social Media & Messaging App Piracy | 71% piracy rate (+13%) |
| Pirate Website Usage | Only 13% of users |
| Pirate TV Box Usage | Only 11% of users |
| Consumer Awareness of Piracy Impact | 89% recognize piracy’s impact |
| Reduction in Piracy (Indonesia) | 59% reduction due to enforcement |
| Reduction in Piracy (Vietnam) | 54% reduction due to enforcement |
| Reduction in Piracy (Malaysia) | 42% reduction due to enforcement |
| Reduction in Piracy (Singapore) | 28% reduction due to enforcement |
VdoCipher’s Anti-Piracy Measures & Hacker Identifications Tool
For years, Hollywood-approved DRM solutions like Google Widevine, Apple FairPlay, and Microsoft PlayReady have been the industry standard for video security. However, piracy techniques have evolved rapidly, making DRM alone insufficient to prevent unauthorized access, illegal downloads, and credential sharing.
At VdoCipher, we go beyond traditional DRM, proactively identifying and blocking piracy attempts before they escalate. Our multi-layered security stack integrates AI-powered piracy tracking, User-based video analytics, and hacker identification to deliver an unparalleled level of protection for content creators, e-learning platforms, and media enterprises.
How VdoCipher Prevents Film Piracy?
Our security-first approach addresses the most critical piracy challenges, ensuring content remains protected across all devices and platforms.
Real-Time Piracy Tracking & Hacker Identification
- Live Monitoring – Detects and auto-blocks piracy attempts, including DRM breaches.
- Session Tracking – Tracks IP addresses, devices, and usage anomalies to flag suspicious behavior.
- Credential Abuse Detection – Identifies users sharing login credentials across multiple devices.
Results from the past 6 months
- 63,210 piracy sessions blocked across various platforms.
- 12,330 unique devices/IPs identified for illegal access attempts.
- 1,690 flagged users for password sharing and overuse.
- 384 accounts proactively blocked by customers.
- Legal actions initiated against repeat offenders.
Advanced Access Control: Stop Video URL Extraction & Unauthorized Playback
- Backend Authenticated Playback URLs – Prevents extracted video links from working outside the intended website/app.
- Secure API-Based Authentication – Ensures videos play only in authorized sessions.
- Geo, Time & Device Restrictions – Restricts playback to specific locations, timeframes, and devices.
Screen Capture Prevention & Dynamic Watermarking
- 100% Screen Capture Block in Mobile Apps & Safari – Protects content from unauthorized recording.
- Dynamic Watermarking – Displays user-specific details (Email, IP, Timestamp) to deter leaks and trace piracy sources.
Telegram & Dark Web Piracy Prevention
- Automated Piracy Detection – Flags unauthorized content sharing on Telegram & piracy forums.
- DMCA & Takedown Support – Works with copyright enforcement teams to remove infringing content.
AI-Powered Analytics to Detect & Block Piracy in Real-Time
- User-Based Analytics Dashboard – Tracks engagement patterns to identify suspicious activities.
- Device & Browser Analysis – Monitors multiple logins from different locations/devices.
- Domain Playback Restrictions – Ensures videos are only played on authorized platforms.
With over 3,000+ platforms across 120+ countries, VdoCipher is the leading provider of secure video hosting, playback, and anti-piracy protection.
FAQs
Are free movie streaming websites safe to use?
No. Many piracy websites are riddled with malware, phishing scams, and data theft risks. Clicking on ads or downloading files from these sites can compromise your personal and financial data.
Can I watch pirated movies if I don’t distribute them?
Watching pirated content is still illegal in many countries, even if you don’t share it. Moreover, accessing pirated websites exposes your device to security threats
How can consumers help fight film piracy?
By choosing legal streaming services, reporting illegal websites, and spreading awareness about the negative impact of piracy, consumers can help reduce its prevalence.
How much revenue do content creators lose due to piracy?
Reports suggest that the entertainment industry loses billions of dollars annually due to piracy. In the e-learning sector, piracy can significantly impact course creators by reducing sales and devaluing premium content.
Supercharge Your Business with Videos
At VdoCipher we maintain the strongest content protection for videos. We also deliver the best viewer experience with brand friendly customisations. We'd love to hear from you, and help boost your video streaming business.


Jyoti began her career as a software engineer in HCL with UNHCR as a client. She started evolving her technical and marketing skills to become a full-time Content Marketer at VdoCipher.

Leave a Reply